Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsushita, Kentaro; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki; Uchida, Mao*; Sakai, Takaaki*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 6 Pages, 2021/05
For the gas entrainment vortex at the free surface in sodium-cooled fast reactors, development of the numerical analysis method to evaluate amount of the gas entrainment from the free surface has been developing. In this paper, the automatic creation of analysis meshes which can suppress the calculation cost while maintaining the prediction accuracy of the vortex shape is investigated, and the adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) method is examined to the creation of analysis mesh applying to the unsteady vortex system. The refined mesh based on the criterion evaluated by vorticity, Q-value as second invariant of the velocity and the discriminant for the eigen equation of the velocity gradient tensor is considered, and it found that the AMR method based on Q-value can refine the analysis meshes most efficiently.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ali, Y.*; Shimokawabe, Takashi*
Proceedings of 9th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems (ScalA 2018) (Internet), p.9 - 16, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:94.51(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)We develop a communication reduced multi-time- step (CRMT) algorithm for a Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) based on a block-structured adaptive mesh refinement (AMR). This algorithm is based on the temporal blocking method, and can improve computational efficiency by replacing a communication bottleneck with additional computation. The proposed method is implemented on an extreme scale airflow simulation code CityLBM, and its impact on the scalability is tested on GPU based supercomputers, TSUBAME and Reedbush. Thanks to the CRMT algorithm, the communication cost is reduced by 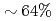 , and weak and strong scalings are improved up to
, and weak and strong scalings are improved up to 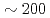 GPUs. The obtained performance indicates that real time airflow simulations for about 2km square area with the wind speed of
GPUs. The obtained performance indicates that real time airflow simulations for about 2km square area with the wind speed of 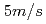 is feasible using 1m resolution.
is feasible using 1m resolution.